vue组件传值和页面间通信传参多种方式,在vue开发时大部分一个页面内父子间组件传参,第二页是跳路由页面间传参,下面解决几种情况不同传参数方法
一、通过路由带参数进行传值
①两个组件 A和B,A组件通过query把orderId传递给B组件(触发事件可以是点击事件、钩子函数等)
this.$router.push({ path: '/conponentsB', query: { orderId: 123 } }) // 跳转到B
②在B组件中获取A组件传递过来的参数
this.$route.query.orderId
二、通过设置 Session Storage缓存的形式进行传递
①两个组件A和B,在A组件中设置缓存orderData
const orderData = { 'orderId': 123, 'price': 88 }
sessionStorage.setItem('缓存名称', JSON.stringify(orderData))
此时 dataB 就是数据 orderData
朋友们可以百度下 Session Storage(程序退出销毁) 和 Local Storage(长期保存) 的区别。
三、父子组件之间的传值,用props
(一)父组件往子组件传值props
①定义父组件,父组件传递 number这个数值给子组件,如果传递的参数很多,推荐使用json数组{}的形式

②定义子组件,子组件通过 props方法获取父组件传递过来的值。props中可以定义能接收的数据类型,如果不符合会报错。
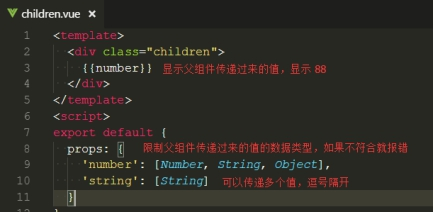
当然也可以简单一点,如果不考虑数据类型,直接 props:["number","string"]就可以了,中括号包裹,多个值使用,分隔。
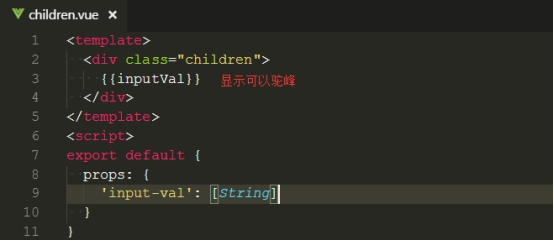
③假如接收的参数 是动态的,比如 input输入的内容 v-model的形式
注意:传递的参数名称 支持驼峰命名,下图 描述不正确(1.0是不支持的)

④父子组件传值,数据是异步请求,有可能数据渲染时报错
原因:异步请求时,数据还没有获取到但是此时已经渲染节点了
解决方案:可以在 父组件需要传递数据的节点加上 v-if = false,异步请求获取数据后,v-if = true
(二)、子组件往父组件传值,通过emit事件
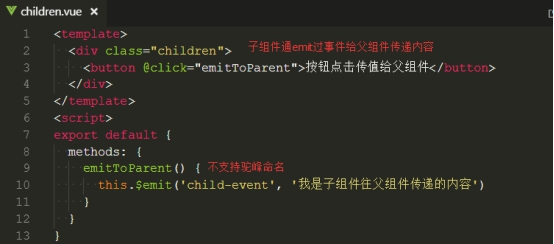
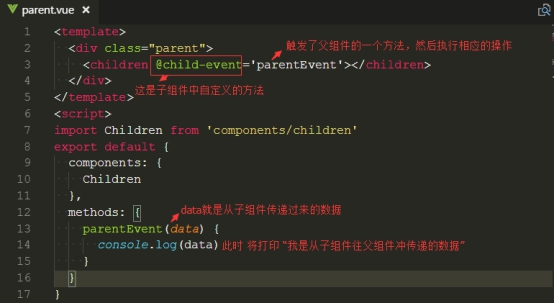
四、不同组件之间传值,通过eventBus(小项目少页面用eventBus,大项目多页面使用 vuex)
①定义一个新的vue实例专门用于传递数据,并导出
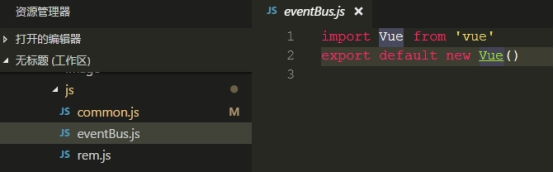
②定义传递的方法名和传输内容,点击事件或钩子函数触发eventBus.emit事件
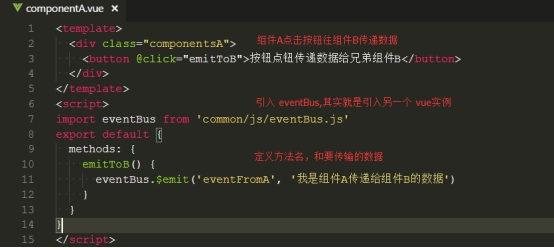
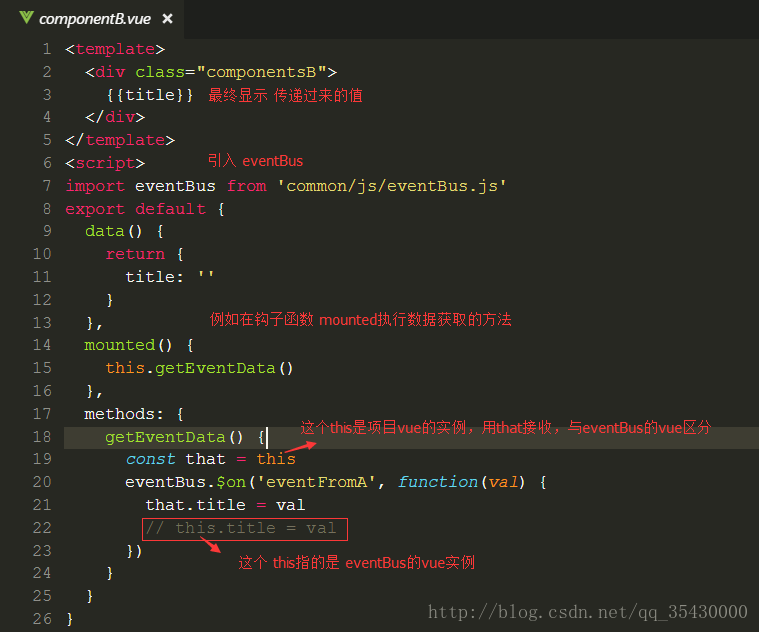
③接收传递过来的数据
注意:enentBus是一个另一个新的Vue实例,区分两个this所代表得vue实例
五、vuex进行传值
为什么使用vuex?
vuex主要是是做数据交互,父子组件传值可以很容易办到,但是兄弟组件间传值(兄弟组件下又有父子组件),或者大型spa单页面框架项目,页面多并且一层嵌套一层的传值,异常麻烦,用vuex来维护共有的状态或数据会显得得心应手。
需求:两个组件A和B,vuex维护的公共数据是 餐馆的名称 resturantName,默认餐馆名称是 飞歌餐馆,那么现在A和B页面显示的就是飞歌餐馆。如果A修改餐馆名称 为 A餐馆,则B页面显示的将会是 A餐馆,反之B修改同理。这就是vuex维护公共状态或数据的魅力,在一个地方修改了数据,在这个项目的其他页面都会变成这个数据。

①使用 vue-cli脚手架工具创建一个工程项目,工程目录,创建组件A和组件B路由如下:
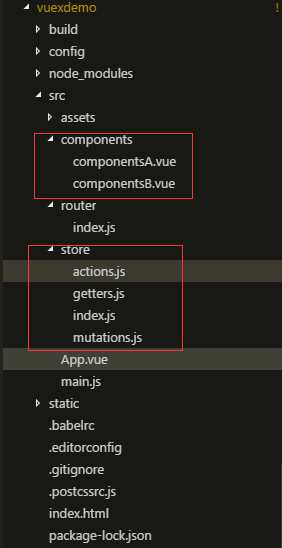
路由如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import componentsA from '@/components/componentsA'
import componentsB from '@/components/componentsB'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'componentsA',
component: componentsA
},
{
path: '/componentsA',
name: 'componentsA',
component: componentsA
},
{
path: '/componentsB',
name: 'componentsB',
component: componentsB
}
]
})
app.vue
②开始使用vuex,新建一个 sotre文件夹,分开维护 actions mutations getters

②在store/index.js文件中新建vuex 的store实例
*as的意思是 导入这个文件里面的所有内容,就不用一个个实例来导入了。
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import * as getters from './getters' // 导入响应的模块,*相当于引入了这个组件下所有导出的事例
import * as actions from './actions'
import * as mutations from './mutations'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 首先声明一个需要全局维护的状态 state,比如 我这里举例的resturantName
const state = {
resturantName: '飞歌餐馆' // 默认值
// id: xxx 如果还有全局状态也可以在这里添加
// name:xxx
}
// 注册上面引入的各大模块
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state, // 共同维护的一个状态,state里面可以是很多个全局状态
getters, // 获取数据并渲染
actions, // 数据的异步操作
mutations // 处理数据的唯一途径,state的改变或赋值只能在这里
})
export default store // 导出store并在 main.js中引用注册。
③actions
// 给action注册事件处理函数。当这个函数被触发时候,将状态提交到mutations中处理
export function modifyAName({commit}, name) { // commit 提交;name即为点击后传递过来的参数,此时是 'A餐馆'
return commit ('modifyAName', name)
}
export function modifyBName({commit}, name) {
return commit ('modifyBName', name)
}
// ES6精简写法
// export const modifyAName = ({commit},name) => commit('modifyAName', name)
④mutations
// 提交 mutations是更改Vuex状态的唯一合法方法
export const modifyAName = (state, name) => { // A组件点击更改餐馆名称为 A餐馆
state.resturantName = name // 把方法传递过来的参数,赋值给state中的resturantName
}
export const modifyBName = (state, name) => { // B组件点击更改餐馆名称为 B餐馆
state.resturantName = name
}
⑤getters
// 获取最终的状态信息 export const resturantName = state => state.resturantName
⑥在main.js中导入 store实例
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store, // 这样就能全局使用vuex了
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
④在组件A中,定义点击事件,点击 修改 餐馆的名称,并把餐馆的名称在事件中用参数进行传递。
...mapactions 和 ...mapgetters都是vuex提供的语法糖,在底层已经封装好了,拿来就能用,简化了很多操作。
其中...mapActions(['clickAFn']) 相当于this.$store.dispatch('clickAFn',{参数}),mapActions中只需要指定方法名即可,参数省略。
...mapGetters(['resturantName'])相当于this.$store.getters.resturantName
<template>
<div class="componentsA">
<P class="title">组件A</P>
<P class="titleName">餐馆名称:{{resturantName}}</P>
<div>
<!-- 点击修改 为 A 餐馆 -->
<button class="btn" @click="modifyAName('A餐馆')">修改为A餐馆</button>
</div>
<div class="marTop">
<button class="btn" @click="trunToB">跳转到B页面</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
##script
import {mapActions, mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'A',
data () {
return {
}
},
methods:{
...mapActions( // 语法糖
['modifyAName'] // 相当于this.$store.dispatch('modifyName'),提交这个方法
),
trunToB () {
this.$router.push({path: '/componentsB'}) // 路由跳转到B
}
},
computed: {
...mapGetters(['resturantName']) // 动态计算属性,相当于this.$store.getters.resturantName
}
}
##script#
<!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only -->
<style scoped>
.title,.titleName{
color: blue;
font-size: 20px;
}
.btn{
width: 160px;
height: 40px;
background-color: blue;
border: none;
outline: none;
color: #ffffff;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.marTop{
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>
B组件同理
<template>
<div class="componentsB">
<P class="title">组件B</P>
<P class="titleName">餐馆名称:{{resturantName}}</P>
<div>
<!-- 点击修改 为 B 餐馆 -->
<button class="btn" @click="modifyBName('B餐馆')">修改为B餐馆</button>
</div>
<div class="marTop">
<button class="btn" @click="trunToA">跳转到A页面</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
##script##
import {mapActions, mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'B',
data () {
return {
}
},
methods:{
...mapActions( // 语法糖
['modifyBName'] // 相当于this.$store.dispatch('modifyName'),提交这个方法
),
trunToA () {
this.$router.push({path: '/componentsA'}) // 路由跳转到A
}
},
computed: {
...mapGetters(['resturantName']) // 动态计算属性,相当于this.$store.getters.resturantName
}
}
##script##
<!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only -->
<style scoped>
.title,.titleName{
color: red;
font-size: 20px;
}
.btn{
width: 160px;
height: 40px;
background-color: red;
border: none;
outline: none;
color: #ffffff;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.marTop{
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>


